What is PoE
What is PoE?
Power over Ethernet (PoE) is a technology that transmits power through network cables. It uses the existing Ethernet to simultaneously transmit data and supply power to IP terminals, such as IP phones, aps, and IP cameras.
PoE is also known as Power over LAN (PoL) or Active Ethernet, and sometimes Power over Ethernet for short.
In order to standardize and promote the development of PoE power supply technology and solve the compatibility problem between power supply and power received devices from different manufacturers, the IEEE Standards Committee has published three PoE standards: IEEE 802.3af, IEEE 802.3at, and IEEE 802.3bt.
Why do we need PoE?
With the increasing availability of IP telephony, network video surveillance and wireless Ethernet devices, it is increasingly urgent to provide power support through Ethernet itself. In most cases, the terminal equipment needs DC power supply, and the terminal equipment is usually installed on the ceiling high above the ground or outside. It is difficult to have a suitable power socket nearby. Even if there is a socket, the AC/DC converter required by the terminal equipment is difficult to locate. In addition, in many large-scale LAN applications, the administrator needs to manage multiple terminal devices at the same time, and these devices need to be managed and powered in a unified manner. Limited power supply locations bring great inconvenience to power supply management. Power over Ethernet (PoE) solves this problem.
PoE is a wired power supply Ethernet technology. The network cables used for data transmission also provide DC power supply. It effectively provides centralized power supply for IP phones, wireless aps, portable device chargers, card readers, cameras, and data collection terminals. PoE power supply has the advantages of reliability, simple connection, and unified standards:
reliable: a PoE device for multiple terminal equipment power supply at the same time, we realize the power of centralized power supply at the same time, also can undertake backup power supply.
connection is simple: terminal equipment without external power supply, only need a piece of string.
standard: in accordance with international standards, the use of global unified RJ45 interface, can guarantee the dock with the equipment of different manufacturers.
How does PoE work?
As shown in the following figure, the PoE power supply system includes the following two device roles:
Power-sourcing Equipment (PSE) : A PoE device that supplies Power to the power supply device over an Ethernet. It provides detection, analysis, and intelligent power management functions, such as a PoE switch.
Powered Device PD (Powered Device) : such as wireless AP, portable device charger, card reader, camera and other powered device. PD is divided into standard PD and non-standard PD according to whether it complies with IEEE standards.
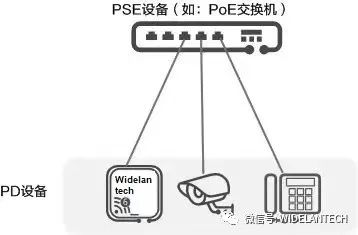
PoE power supply mode
According to the IEEE standard, PSE devices are classified into MidSpan (where the PoE function module is outside the device) and Endpoint (where the PoE function module is integrated inside the device).
The PSE device with the Endpoint type can be divided into Alternative A (1/2 and 3/6 wire pairs) and Alternative B (4/5 and 7/8 wire pairs) power supply modes depending on the power supply pairs used.
Alternative A Power supply mode supplies power through data pairs. PSE supplies power to PD through 1/2 and 3/6 wire pairs, with a 1/2 link forming a negative terminal and a 3/6 link forming a positive terminal. 10BASE-T and 100BASE-TX interfaces use 1/2 and 3/6 wire pairs to transmit data, and 1000BASE-T interfaces use all 4 wire pairs to transmit data. Because DC and data frequencies do not interfere with each other, current and data can be transmitted simultaneously on the same pair of lines.
Alternative B Power supply mode Power is supplied through idle pairs. PSE supplies power to PD through 4/5 and 7/8 wire pairs, with 4/5 links forming positive terminals and 7/8 links forming negative terminals.
The IEEE standard does not allow the use of these two power supply modes simultaneously. The powering device PSE can only provide one use, but the receiving device PD must be able to accommodate both situations.
PoE power supply negotiation process
After the PSE device is powered on and the PD device is connected to the PSE device through the network, PSE and PD begin power supply negotiation:
detecting PD: PSE on port periodic voltage output current limited small, used to detect the presence of PD equipment. If a specific resistance is detected, the cable terminal is connected to a receiving device that supports the IEEE 802.3af or IEEE 802.3at standards. (The resistance ranges from 19kΩ to 26.5 kω, with a minimum voltage of 2.7V to 10.1V, and the detection period is 2 seconds.)
power supply ability to negotiate the PD equipment classification process: PSE categorize PD, and negotiating power. Power supply capability negotiation can be realized not only by parsing the resistors sent by PSE and PD, but also through the Link Layer Discovery Protocol (LLDP).
start power supply: during the start period (usually less than 15 mu s), PSE equipment start from low voltage supply power to PD equipment to provide 48 v dc voltage.
normal power supply, the voltage reached 48 v, after PSE for PD device to provide stable and reliable for 48 v direct current, PD equipment power consumption less than PSE maximum output power.
power: the power supply in the process, PSE is constantly monitoring PD input current, when PD under current consumption dropped to the lowest, or current surge, unplug the equipment or meet PD equipment power consumption such as overload, short circuit, over the power supply and load of PSE, PSE will disconnect the power supply, and repeat the process.
The LLDP protocol is used to negotiate the power supply capability
IEEE 802.1ab defines an optional Type Length Value (TLV) : Power via Media Dependent Interface (MDI) TLV. LLDP packets are encapsulated with Power via MDI TLVS to discover and notify the MDI power supply capability. After PSE detects PD, PSE and PD periodically send LLDP packets containing the defined TLV field to each other. The local end sends information to the peer end, and the peer end records the information contained in the packet.
However, the Power via MDI TLV format defined by IEEE 802.1ab can only negotiate the power supply parameters of IEEE 802.3af and IEEE 802.3at standards, but cannot negotiate the power supply parameters of IEEE 802.3bt standards. When connected PD devices use IEEE 802.3bt standard Power supply, the standard Power via MDI TLV will not be able to negotiate power supply.
Power via MDI TLV packets defined in IEEE 802.1ab
It consists of a 2-byte TLV header and a 12-byte TLV information field. The format of the packet is shown as the following figure:
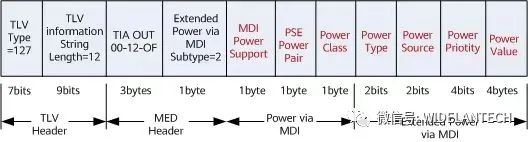
TLV packet Format defined by IEEE 802.1ab The following figure shows the meanings of the fields Power via MDI and Extended Power via MDI.
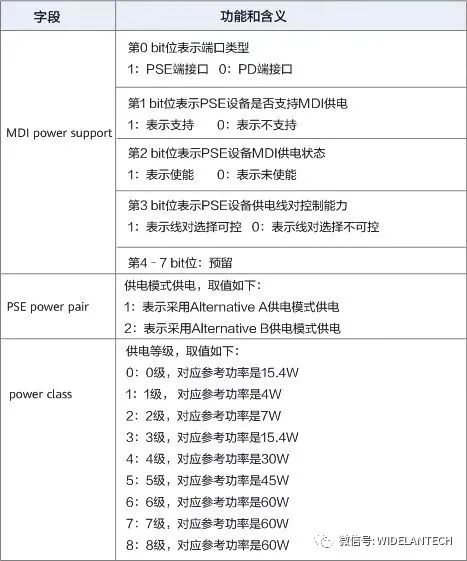
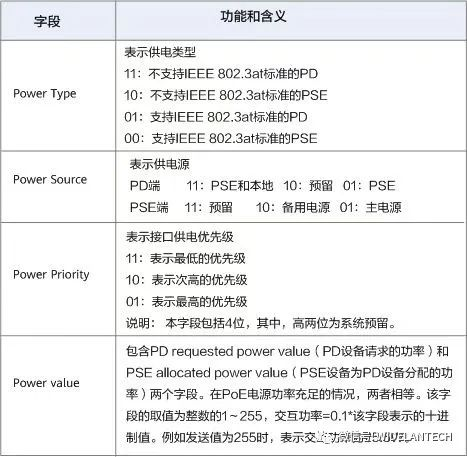
What are the PoE power supply standards?
As mentioned above, the IEEE Standard Committee has issued three PoE standards: IEEE 802.3af, IEEE 802.3at, and IEEE 802.3bt to solve the compatibility problem between power supply and power received devices from different manufacturers. So what's the difference between these three criteria?
In June 2003, the IEEE 802.3af standard was developed by the IEEE 802.3AF Working Group. As an extension of the Ethernet standard, the network power supply, transmission and reception are specified in detail. For example, the IEEE 802.3af standard states that PSE devices need to provide up to 15.4W of DC power per port.
Due to some power dissipation in the cable, only 12.95W of the receiving equipment is available. In October 2009, IEEE 802.3at standard was born to meet the needs of high power terminals. Based on compatible 802.3af standard, IEEE 802.3at standard provides up to 25.5W of power to meet the new needs.
In September 2018, in order to further improve PoE power supply and optimize the standard, IEEE Standards Committee published IEEE 802.3bt standard. The IEEE 802.3bt standard further improves power supply, with Type 3 providing up to 51W and Type 4 providing up to 71.3W. Also included is support for 2.5GBASE-T, 5GBASE-T, and 10GBASE-T, expanding the use of applications such as high-performance wireless access points and surveillance cameras.
Generally, the power supply technology corresponding to IEEE 802.3af standard is called PoE power supply, the power supply technology corresponding to IEEE 802.3at standard is called PoE+ power supply, and the power supply technology corresponding to IEEE 802.3bt standard is called POE+ + power supply, also known as 4PPoE. The following figure shows the corresponding parameters of the three power supply technologies.


